Evapotranspiration and transpiration, both processes play a vital role in agricultural practices. Gardeners should understand the difference between both processes to adjust irrigation schedules.
Many people consider them the same process however this is not true. When you know the water cycle, you can manage the conditions of the greenhouse which prevents many plant diseases and pathogens growth.
If you want to nurture healthy vegetation in your greenhouse, you must understand the difference between evapotranspiration and transpiration. This guide will explain everything about both processes.
What is Transpiration?
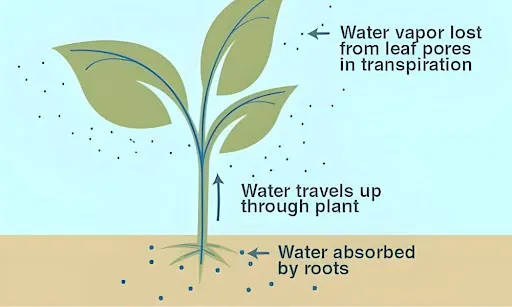
Transpiration is the process through which water leaves the plant and enters the atmosphere. The water enters the plant from soil and leaves the plant through the stomata to the atmosphere. This is a continuous physiological process.
The plant absorbs water from the soil and transports it to the leaves through the xylem. Only 5% of water remains in the plant while the surplus water absorbed by the plant is dissipated through stomata.
The process plays an important role in maintaining the temperature of the plant as it keeps the plant cool.
Types of Transportation
There are three main types of transpiration depending on the place where the process is taking place.
- Stomatal Transpiration: Stomata are small openings present on the surface of leaves. Stomata covers about 3% of the surface area of the leaf and allows gaseous exchange. These openings let the water leave the plant and evaporate outside which is stomatal transpiration.
- Lenticular Transpiration: In this process, transpiration occurs through the openings which are present in barks of some plants.
Cuticular Transpiration: The water loss occurs through the cuticles which are waxy layers present on the surface area of the leaf.
Factors Affecting The Transpiration
There are many factors like climate and soil which regulate the rate of transpiration inside your greenhouse.
According to research, an increase in radiation, temperature and air movement enhances transpiration and high relative humidity lowers the rate of transpiration.
Temperature
The temperature has a direct relation with the rate of transpiration. Higher temperature means higher transpiration and vice versa.
Humidity
Plants need moderate or comfortable humidity ranges for the growth of the plant. If the humidity is higher, the plant can’t transpire. Similarly if the rate of transpiration is too low, the plant will close its stomata to conserve the water.
Light
The increase in light means the more heat which leads to the higher rates of transpiration. The light also affects the opening of stomata, an opening involved in the rate of transpiration. More light leads to wider opening of the stomata. It increases the surface area for gaseous exchange and transpiration.
Air Movement
The good airflow in the greenhouse reduces the humidity levels and also increases the rate of transpiration. Because the wind carries the water vapor away from the leaves.
In addition to the environmental factors, the morphological traits of plants like leaf alignment, area and shape also determine the rate of transpiration.
What is Evapotranspiration?
Evapotranspiration is the union of all the processes through which water circulates from soil to the atmosphere. These processes include transpiration and evaporation through which water changes into gas in the greenhouse. The process serves a critical purpose in balancing energy and agricultural practices.
- Evaporation: This is the process through which water vapourizes into the atmosphere. The water is moved from the soil, groundwater and water bodies to the atmosphere.
- Transpiration: Transpiration is the movement of water from soil to plant and then dissipates into the atmosphere.
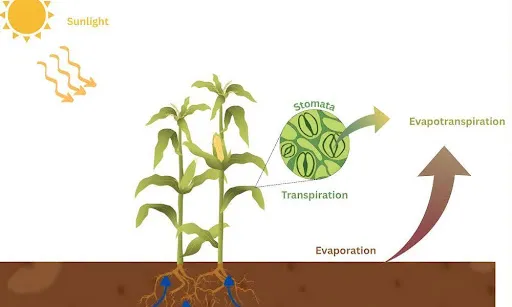
The evapotranspiration rate gives an estimate about how much water is absorbed by the crops, to schedule watering practices and for watershed management. The process also provides a cooling effect as the places with higher evapotranspiration rate are cooler than other areas.
Factors Affecting The Evapotranspiration
According to a study, the humidity and dew point affected the evapotranspiration for the year of 2018 and 2019. Wind speed has less impact while pressure doesn’t affect the evapotranspiration much.
There are several factors that affects the rate of evapotranspiration, some of them are:

1. Humidity
The moisture levels inside the greenhouse determine the rate of evapotranspiration. Low humidity levels increase the evapotranspiration. The ability to take water up by the atmosphere also impacts evapotranspiration.
Fans, vents and airflow remove the extra moisture and raise the rate of evapotranspiration. You can consider using a dehumidifier as it can maintain the humidity levels required for healthy plants growth and prevents higher moisture in a greenhouse.
2. Energy
The higher energy means the higher rate of evapotranspiration. You can introduce artificial light in your greenhouse as it increases plant activity and water loss as well. Intense sunlight also elevates the rate of evapotranspiration.
3. Water Availability
The availability of water in soil is the fundamental factor for evapotranspiration. The dry soil reduces this process. There is no evapotranspiration if there is no water supply.
4. Type of Vegetation
The type of vegetation alters the rate of evapotranspiration. The leafy plants have less dense foliage than woody plants so they require less water. Similarly, the plants with extensive roots absorb more water from the soil.
5. Plant Density
Crowded plants create a micro environment inside the greenhouse which increases the humidity levels. This leads to lower rates of evapotranspiration.
The greenhouses are made up of materials like glass and plastic. This nature of material also determines the rate of evapotranspiration.
The Difference Between Evapotranspiration and Transpiration

By knowing the difference between evapotranspiration and transpiration, you can manage water needs of your plants. Here is the quick data table of the difference between evapotranspiration and transpiration;
Feature | Evapotranspiration | Transpiration |
Definition | Total water loss from land surface and plants combined | Water loss only from plant leaves |
Components | Evaporation and transpiration | Only transpiration |
Source of Water Loss | Soil, water bodies and plants | Plant leaves and stems |
Process Type | Combination of physical and biological processes | Entirely biological process |
Influencing Factors | Sunlight, wind, temperature, soil moisture, plant type | Plant health, stomatal opening, humidity, temperature |
Measurement | Used in hydrology and irrigation planning | Used in plant physiology studies |
Scale | Landscape or ecosystem level | Individual plant level |
Impact on Environment | Affects water cycle and climate | Affects plant growth and cooling |
Example | Moisture rising from soil and plants in a field | Moisture released by leaves of a tree |
Conclusion
Transpiration is the movement of water from soil to atmosphere through plants while evapotranspiration is the sum of all processes through which water changes into vapours.
Transpiration and evapotranspiration are the most important conditions to maintain, no matter if you’re growing plants indoors or outdoors. If you regulate both processes you can get more yield and better quality fruits.
If you want to improve both processes to their ideal condition for plant growth, we suggest you use Coairo Dehumidifiers inside the greenhouse to maintain ideal humidity levels.


